INDIA
1.
In the north, it is bound by
the lofty Himalayas.
2.
The Arabian Sea in the west
3.
The Bay of Bengal in the east
and the Indian Ocean in the south
4.
The north-south extent from
Kashmir to Kanyakumari is about 3,200 km.
5.
And the east-west extent from
Arunachal Pradesh to Kutch is about 2,900 km.
LOCATIONAL SETTING
1.
India is located in the
northern hemisphere
2.
The Tropic of Cancer (23°30 ' N)
passes almost halfway through the country
3.
From south to north,
India extends between 8°4' N and37°6' N latitudes.
4.
From west to east,
India extends between 68°7 ' E and97°25 'E longitudes.
5.
The southernmost point of
the Indian Union– ‘Indira Point’ got submerged under the sea water in 2004
during the Tsunami.
SIZE
1.
An area of 3.28 million square
km.
2.
India’s total area accounts
for about 2.4 per cent of the total geographical area of the world.
3.
India is the seventh
largest country of the world.
4. India has a land boundary
of about 15,200 km
5.
The total length of the coast line of the mainland including Andaman
and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
6.
India is bounded by the young
fold mountains in the northwest, north and north east.
7.
From Gujarat to Arunachal
Pradesh there is a time lag of two hours.
8.
Hence, time along the Standard
Meridian of India (82°30'E) passing through Mirzapur (in Uttar Pradesh)
is taken as the standard time for the whole country.
9. Rajasthan is the
largest state
10.
Goa is the smallest state in terms of area.
11.
No other country has a long
coastline on the Indian Ocean as India has and indeed, it is India’s eminent
position in the Indian Ocean which justifies the naming of an Ocean after it.
12.
Since the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, India’s distance from Europe has
been reduced by 7,000 km.
Do
you know?
1.
The USA and Canada have six
time zones extending from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast.
2.
The local time changes by four
minutes for every one degree of
longitude.
3.
The local time of longitude of
82°30' E has been taken
as the Indian Standard Time.
INDIA’S NEIGHBOURS
1.
There are seven countries that share land
boundaries with India
2.
Across the sea to the south,
lie our island neighbours— Sri Lanka and Maldives.
3.
Sri Lanka is separated from
India by the Palk Strait.
India shares its land boundaries with
1.
Pakistan
2.
Afghanistan
3.
China (Tibet)
4.
Nepal
5.
Bhutan
6.
Myanmar
7.
Bangladesh
Two
island countries
1.
Sri Lanka
2.
Maldives
PHYSICAL FEATURES
OF INDIA
1.
Most volcanoes and earthquakes
in the world are located at plate margins, but some do occur within the plates.
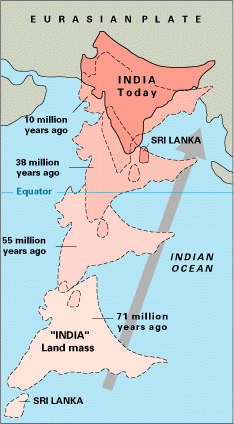
2.
The oldest landmass, (the Peninsula
part of India), was a part of the Gondwana land.
3.
The Gondwanaland included India,
Australia, South Africa and South America as one single land mass.
4.
The convectional currents split
the crust into a number of pieces.
5.
This leads to the drifting of
the Indo-Australian plate after being separated from the Gondwana land, towards
north.
6.
The northward drift resulted in
the collision of the plate with the much larger Eurasian Plate
7.
Due to this collision, the
sedimentary rocks which were accumulated in the geosynclines known as the
Tethys were folded to form the mountain system of western Asia and Himalaya.
What is Gondwanaland?
1.
It is the southern part of the
ancient super continent Pangea with Angara Land in the northern part.
2.
The Himalayan uplift out of the
Tethys Sea and subsidence of the northern flank of the peninsular plateau
resulted in the formation of a large basin.
3.
In due course of time this
depression, gradually got filled with deposition of sediments by the rivers
flowing from the mountains in the north and the peninsular plateau in the
south.
4.
A flat land of extensive
alluvial deposits led to the formation of the northern plains of India.
5.
Geologically, the Peninsular
Plateau constitutes one of the ancient landmasses on the earth’s
surface.
Next
Next
.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment